Data-Driven Aerodynamics
Deep Learning Applications to Airfoil Performance Prediction and Inverse Design, Deep ConvNets, cGANs
ConvNets for Airfoil Performance Prediction
- Medium-fidelity predictors were trained for predicting airfoil performance using deep convolutional neural networks. The framework was implemented in Tensorflow.
- Published a conference paper: AIAA Aviation’17 (Yilmaz & German, 2017).
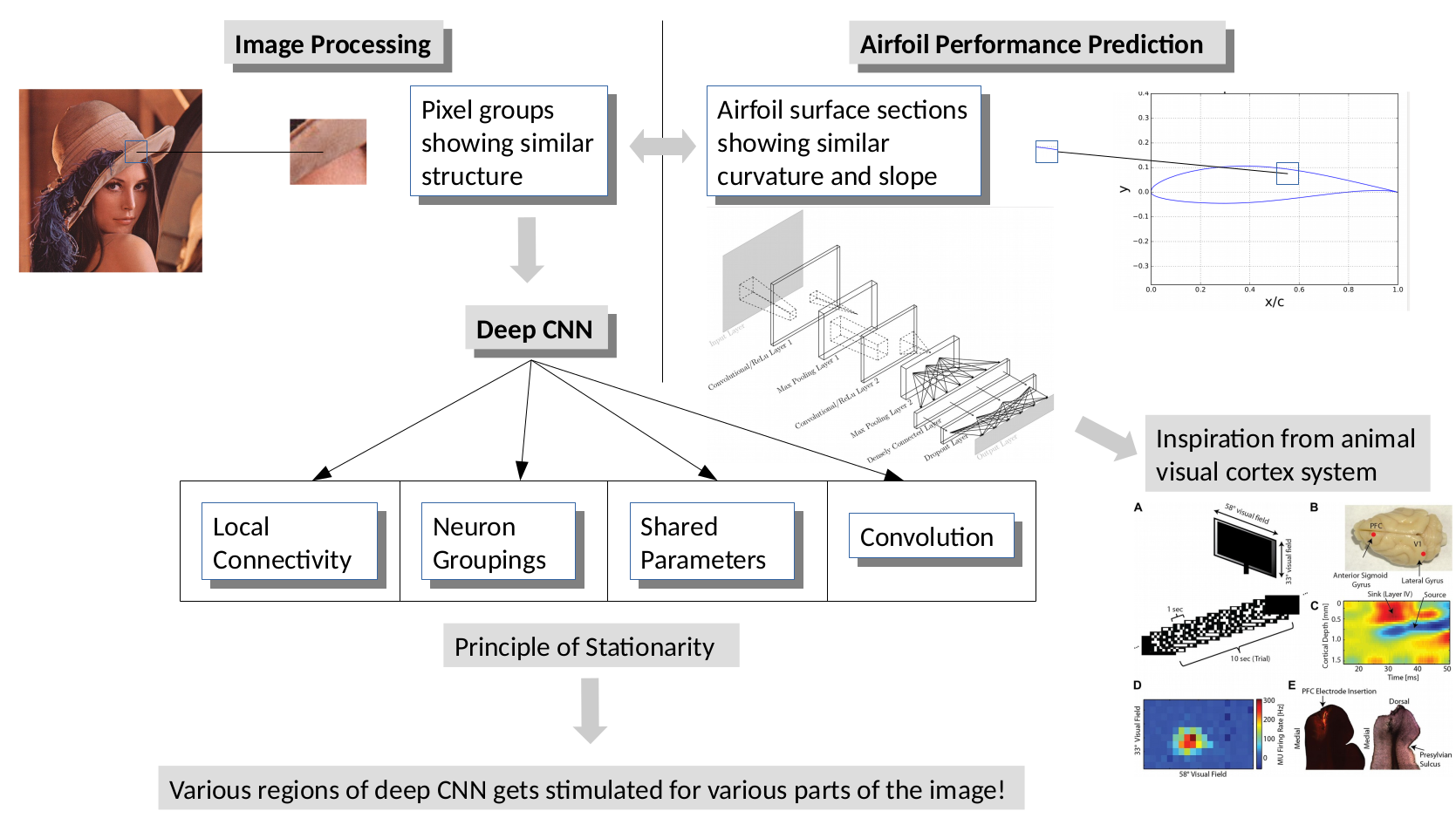
The Application of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks to Airfoil Performance Prediction
ConvNets for Airfoil Inverse Design
- Airfoil inverse problem was reformulated and solved using a framework constructed with deep convolutional neural networks.
- Published a conference paper: AIAA Aviation’18 (Yilmaz & German, 2018).
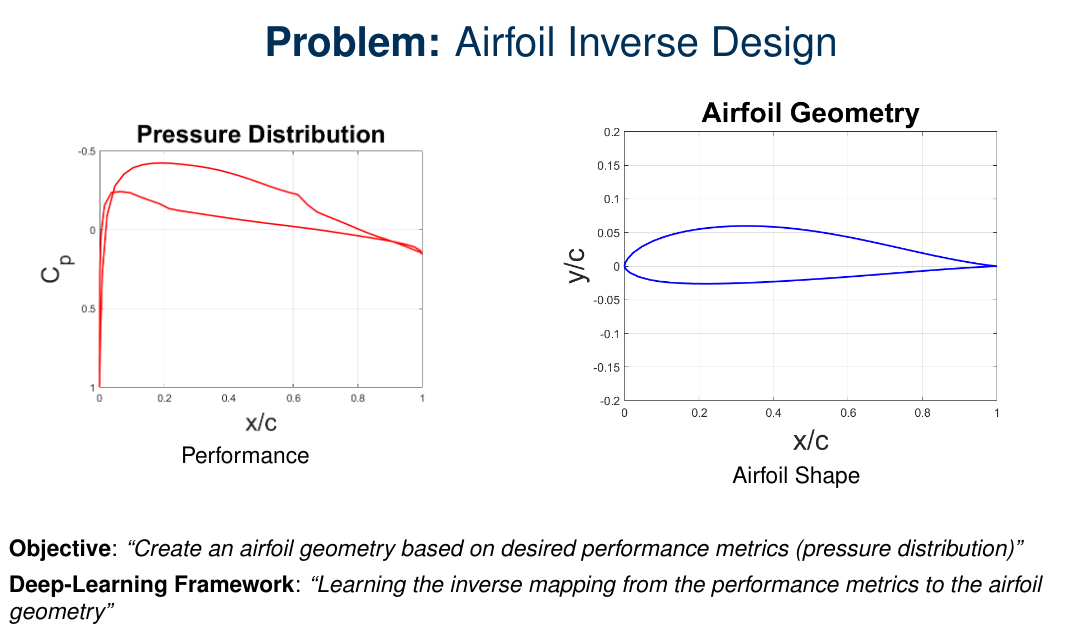
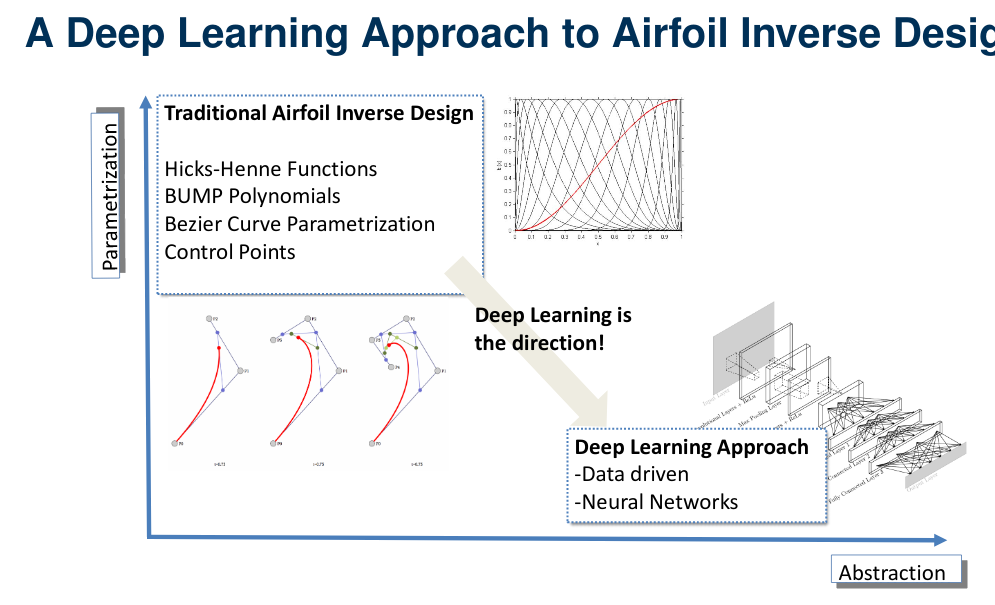
The Application of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks to Airfoil Inverse Design
CGANs for Airfoil Inverse Design
- A game theoretic framework was investigated by training conditional generative adversarial networks (CGANs) to generate airfoil shapes given the desired airfoil performance criteria.
- Published a conference paper: AIAA Aviation’20 (Yilmaz & German, 2020).
- Funding Proposal Experience
-ARPA-E: DIFFERENTIATE (Design Intelligence Fostering Formidable Energy Reduction and Enabling Novel Totally Impactful Advanced Technology Enhancements) Program.
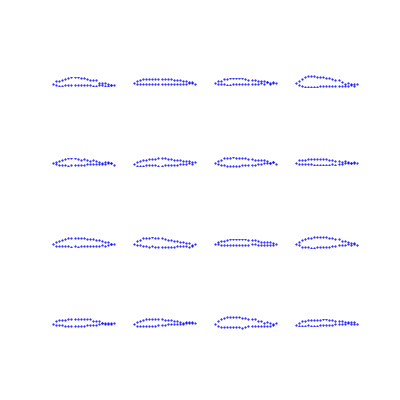
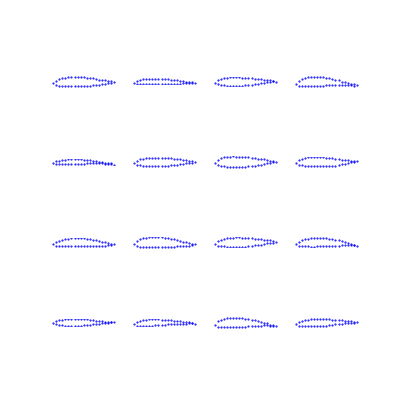
Airfoil Shape Generation by the Generator in GAN Framework Shown at Different Epochs
